Blood flow changes in the brain due to fatigue
During sleep restriction there is reduced functional connectivity between the emotion regulation centre and the emotion processing centre. This increases emotional reactivity to negative stimuli.
Generally, the frontal lobes provide inhibition to the amygdala. However, when the amygdala is activated, “amygdala hijack” can result in emotional overload and impaired rationality, leading to rapid, unthinking reactions.
Amygdala
The amygdala serves as a central hub for:
- Emotion
- Memory
- Decision-making
- Social cognition
- Plays a key role in processing fear, aggression, and anxiety
- Triggers the flight, fight or freeze response
Sleep deprivation can reduce emotional regulation leading to rapid, unthinking reactions.
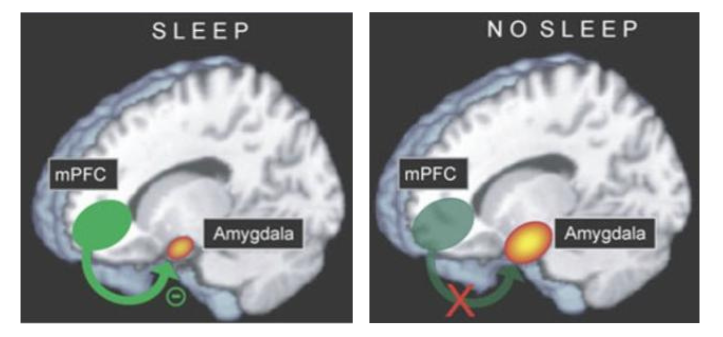
The image to the right, shows amygdala activation after no sleep for 24-hours. It can increase by up to 60%.
Sleep deprivation led to loss of functional connectivity between mPFC and amygdala which can reduce emotional regulation.
mPFC (Median Prefrontal Cortex)
Crucial brain region involved in a wide range of functions including:
- Decision-making
- Memory
- Social cognition
- Emotional regulation
- Modulates stress responses
IMPACT OF INADEQUATE SLEEP:
- Increases fear response
- Lowers inhibition
- Enhances impulsivity to negative stimuli
- Alters emotional regulation: Irritability, emotional reactivity, poor social interactions
Amygdala Hijack Video
It is the result of emotional overload resulting in: Impaired rationality, leading into rapid, unthinking reactions.
Sleep deprivation lowers inhibition and enhances impulsivity to negative stimuli
“Inadequate sleep increases fear response”
Source: Science Direct